Battery energy storage boosts PV power in smart grid
Distributed on-grid PV systems with battery energy storage can effectively ‘time-shift’ production
MICHAEL LIPPERT
Saft Energy Storage Systems
www.saftbatteries.com
The ever-increasing political and environmental pressure for the power generation industry to meet demanding climate and energy targets is driving the increased use of renewable energy sources such as wind and solar power. As a result, electricity generation is becoming more decentralized and more intermittent. This calls for new types of power grids with both the flexibility and intelligence to receive generation of all qualities and quantities from diverse sources, and the capability of managing them to deliver reliable consumer supplies.
A specific area where energy storage is set to make an early impact on smarter grids is in helping to boost self-consumption in grid-connected solar PV (photovoltaic) installations.
Boosting self-consumption
PV installations with a permanent connection to the electricity grid are categorized as “on-grid” applications. This is currently the most popular type of PV system for homes and businesses in the developed world, comprising more than 90% of all PV installations. According to the Energy Information Administration, the average household electricity consumption in 2001 was 10,654 kWh. The typical residential (see Fig. 1 ) PV array in the USA is around 4kW, which is sufficient to make more efficient homes ‘zero energy’ or self-sufficient in terms of energy use. However, unless net metering is allowed, the current practice is to inject all of the PV energy produced by domestic schemes into the local electricity network, to be sold to the local utility. The household still imports all the electricity it needs from the network.
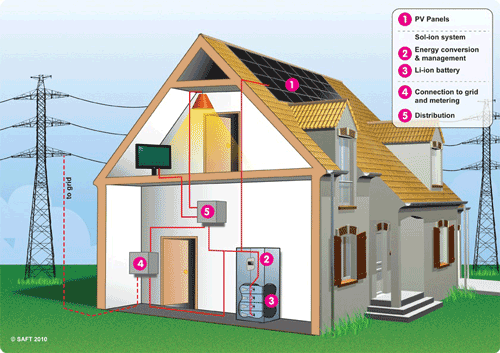
Fig. 1: Typical residential PV array with net metering.
In the near future, it is expected that we will see a significant change in this operating model as households aim to become energy autonomous. This means that they will both produce and consume their own electricity, using a local energy storage system to store any excess PV energy until it is needed. In essence, the PV energy produced will need to be ‘time-shifted’ from the daytime, peaking at noon, to make it available on demand in the evening. Converting daytime solar power into a usable form during non-daylight hours requires an energy storage system.
The operational model
A typical U.S. residential PV system with a panel size of 4 kW produces a daily average of 18 kWh throughout the year, ranging from 8 kWh in winter to a peak of 24 kWh in summer. Some of the PV energy will be used directly (self-consumed), as soon as it is produced. This produces an excess of energy ranging from 2 to 8 kWh that can then be stored until needed. An energy storage system will need to ‘time-shift’ an average of about 5 kWh per day.
Li-ion technology
In grid-connected energy storage applications, the newest practical battery technology, lithium-ion (Li-ion), offers the potential for significant improvements in terms of performance and service life over conventional storage batteries, and it is also zero-maintenance. Although Li-ion batteries are very well established in consumer applications, the ordinary consumer cells are not suitable due to the more rigorous demands of PV applications. Instead, a new generation of Li-ion battery systems designed specifically for industrial applications is under development, with the first systems already on field test.
The compact, sealed-for-life design of Li-ion batteries offers considerable advantages. Field tests are confirming that Li-ion technology will offer very high efficiency, around 95%, combined with a long calendar and cycle life, 20 years at 60% DOD (depth of discharge)/day. Compact domestic Li-ion batteries would have a small footprint, comparable to 13 gallons and about the size of a kitchen trash can (considering a minimum capacity of 5 kWh).
Projects in the U.S.
Saft Li-ion batteries will supply renewable energy storage for the Sacramento Municipal Utility District’s (SMUD) PV storage pilot program at Anatolia, Ill, a high penetration PV community within SMUD’s service territory. The two-year pilot project is being funded by the DOE to examine the value of distributed PV coupled with energy storage in 15 homes and three sites on SMUD’s distribution system within the community. Efficient energy storage will enable solar power to be time-shifted (see Fig. 2 ) to support SMUD’s “super-peak” from 4 p.m. to 7 p.m., particularly when PV output drops off after 5 p.m.
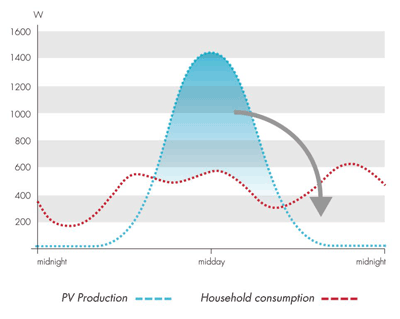
Fig. 2: Energy storage allows solar power to be time shifted to support super-peak hours.
Another example is the 2500 R Street project, a sustainable and efficient 34-home community in Sacramento. The homes are part of California’s first micro-grid, distributed energy community housing project designed to meet stringent energy-efficient guidelines. Saft Li-ion batteries will supply renewable energy storage. These advanced homes will use the latest in smart grid, solar generation and energy storage to ensure each home generates as much clean energy as it uses, thus maximizing homeowner utility bill savings.
Energy storage systems will be used in each of these projects to capture solar energy and store it for use when needed most. Li-ion is the only battery technology that meets the need for 20-year battery life and the ability to withstand a range of demanding environmental conditions.
There is a clear demand across the globe for renewable energy sources, which requires a new type of grid. Energy storage is a vital element in creating the smart grid of the future with the flexibility and intelligence to receive generation from various sources with reliable delivery. Distributed on-grid PV systems with battery energy storage can effectively ‘time-shift’ production, making electrical power available when it is needed. Li-ion offers a promising energy storage technology and successful trials are leading us closer to the reality of fully producing and consuming our own household electricity. ■
Advertisement
Learn more about Saft Batteries





