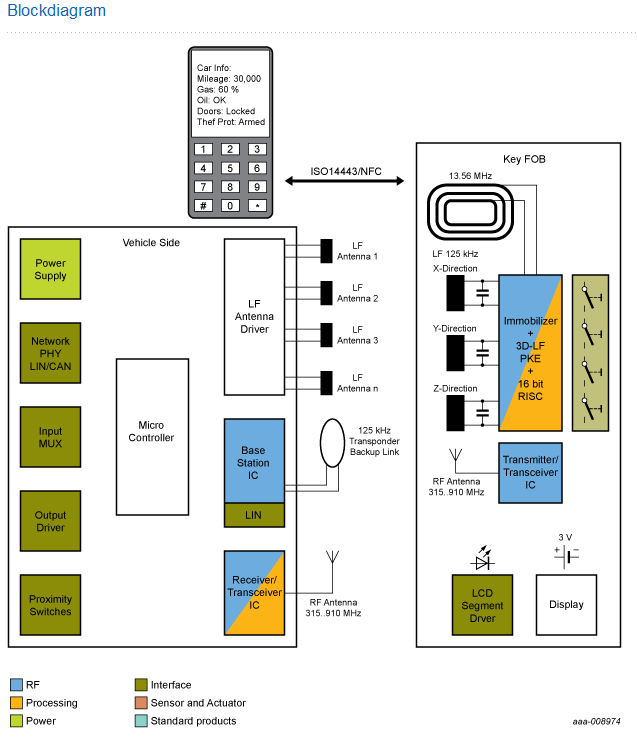
NXP is the leading automotive supplier of chipset solutions for PKE and PKG systems worldwide, characterized through low power consumption while granting high LF sensitivity and maximized reading distance. Minimized key FOB designs can be realized by our high level of integration, including the 3D active LF frontend, wakeup-processor, backup immobilizer and 16-bit RISC for processing of remote keyless entry (RKE), PKE and PKG.
How the passive keyless entry system works
Communication is initialized between the car and the key FOB by pulling the door handle. The authentication process begins when the car measures the received 125 kHz signal strength (RSSI), which determines the key FOB's position. If the key FOB is within a defined area outside the car and passes authentication, the car unlocks the door.
A similar procedure takes place for passively starting the engine except the key FOB needs to be within a defined area inside the car.
An immobilizer backup mode provides the means to start the car in the case of a drained battery. Within this mode, the IC is powered by a 125 kHz field and does not need an external power supply.
Additional interfaces
With MantraC, the highly integrated single chip transceiver IC, NXP enables advanced applications using 2-way RF communication via 315..910 MHz radio link. Remote engine start, remote read out of car status (such as tire pressures, fuel level, door lock status) and lock feedback can easily be realized.
The integration of an ISO14443 interface within NXP’s KeyLink product range makes the next generation car key interoperable with NFC enabled mobile phones or card readers for a variety of new use cases. Car status information can be displayed on a mobile phone or routes can be planned in advanced and saved on the car key.
Download Full Block Diagram Below
Advertisement

Learn more about NXP Semiconductors





