Pulse oximeter is a non-invasive medical device that monitors the oxygen saturation of a patient’s blood and heart rate. This application note demonstrates the implementation of a high-accuracy pulse oximeter using Microchip’s analog devices and dsPIC® Digital Signal Controllers (DSCs).
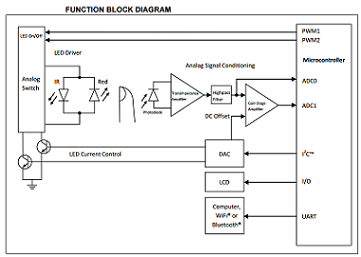
A pulse oximeter monitors the oxygen saturation (SpO2 ) of a human’s blood based on the red light (600- 750 nm wavelength) and infrared light (850-1000 nm wavelength) absorption characteristics of oxygenated hemoglobin (HbO2 ) and deoxygenated hemoglobin (Hb). The pulse oximeter flashes the red and infrared lights alternately through a finger to a photodiode. HbO2 absorbs more infrared light and allows more red light to pass through. On the other hand, Hb absorbs more red light and allows more infrared light to pass through. The photodiode receives the non-absorbed light from each LED. This signal is inverted using inverting OpAmp and therefore the result, as shown in Figure 2, represents the light that has been absorbed by the finger.
Click here for Application Note
Download full block diagram below
Advertisement

Learn more about Microchip Technology





