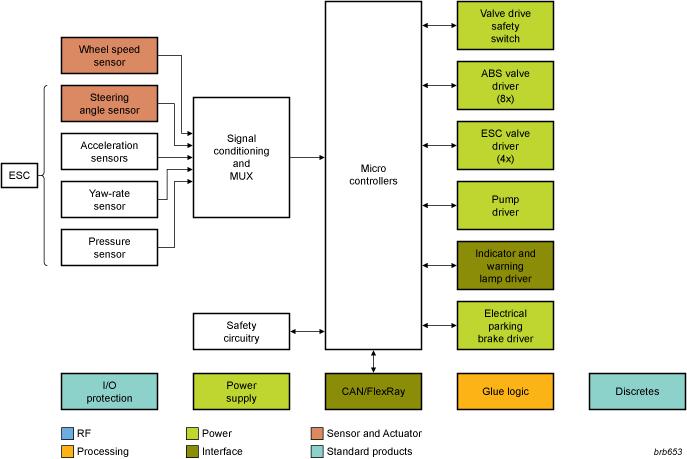
To ensure proper vehicle control during braking and reduce stopping distance, most vehicles have ABS and ESC on board to increase the safety of passengers. Based on different sensor input signals, the precise control of the hydraulic modulator ensures that each wheel has the right braking force at the right time. The fault statuses are monitored by the control unit and displayed to the driver. The electric park brake option further enhances vehicle safety and driver comfort.
Driving valves, pump and motor
The required load currents in a braking system go from several mA , for driving LEDs to display the status and operating mode in the instrument cluster, up to more than 20 A for driving pumps or motors. NXP offers discrete solutions such as small-signal MOSFETs or low VCEsat (BISS) transistors, constant current sources (PSSI) and logic devices for small loads. Power MOSFET devices in advanced TrenchMOS technology will control the various ABS, ESC valves and the safety switch as well as the ABS pump or the DC motor for the electric park brake. For example, the highly innovative LFPAK devices have a footprint 46% smaller than that of DPAK, while offering similar thermal performance. In addition, TrenchPLUS is a range of standard MOSFETs with added protection features, including current and temperature sensing components, overvoltage clamps and gate protection (ESD) diodes. All of these products have some characteristics in common, with low conduction losses and innovative packages to save board space and provide cost-effective solutions.
In-vehicle communication
Besides offering standalone transceivers for all networking protocols, such as braking systems with CAN and FlexRay with advanced functionality such as failure management and power saving, NXP offers highly integrated in-vehicle-networking products such as our system basis chip (SBC) families. The UJA10xx devices combine one or several bus transceivers, voltage regulators, I/O pins and the option of a watchdog in a single IC. The combination of these integrated functions offers advanced low-power mode control and smart fail-safe behavior. Pin compatible family devices with different transceiver options support scalable platforms by simply changing the population of the printed circuit board.
Magnetoresistive Sensors
Magnetoresistive (MR) rotational speed sensors are widely used in braking systems to measure the wheel speed and NXP provides customized solutions. The ESC system uses in addition several sensors to find out what the driver wants. The contactless steering angle sensor is one of the most important sensors and NXPs MR based solutions out of the KMZ overcome the limitation of optical sensor based systems.
These MR devices provide an output signal virtually independent of magnet tolerances, magnet temperature coefficients, magnet-sensor distance and positioning tolerances, guaranteeing reliability and simplifying your manufacturing process.
I/O protection
NXP offers a series of ESD protection devices out of the PESD family, specifically designed to protect automotive networks. The MMBZ series offers single line bidirectional or dual-line unidirectional transient overvoltage protection in a small SOT23 package. Surge protection up to 600W is assured by the Transient Voltage Suppressor (TVS) product family.
Low Ohmic Power MOSFET devices in advanced TrenchMOS technology allow robust reverse polarity protection.
Glue logic
Beside a complete portfolio of standard logic products with different supply voltage range and speed in innovative packages, NXP offers dedicated devices as low Ohmic analog switches, analog and digital multiplexers and I/O expansion devices to strive for cost optimized braking solutions.
Download Full Block Diagram Below
Advertisement

Learn more about NXP Semiconductors





