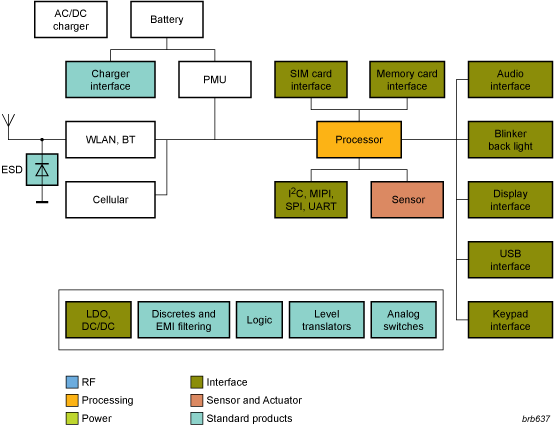
NXP aligns their key considerations for e-book design with the user requirements. They must have a slim form factor, long battery times, access to books everywhere, good audio quality, compatibility with standardized interfaces (USB, Memory Cards) and a robust design.
EMI-filter with ESD-protection
The increasing complexity in mobile applications has lead to an increase in interface signal frequencies, external interfaces and, especially, an increase in consumers who rely on their in mobile devices. For user accessible interfaces, a rugged ESD protection is mandatory to avoid damage or failure of the mobile.
The increase in signal speed/frequency leads to EMI radiation from signal busses operating at higher frequency ranges. For example, the microSD card bus speed up to 100MHz clock and MIPI lanes with 600 MHz and more. The increase in fundamental bus frequencies leads to a growing importance of EMI-filtering to minimize harmonic frequencies within the mobile communication bands.
Memory Card Interfaces
According the IEC61000-4-2 standard, SD host interfaces require additional high-level ESD protection, in addition to the integrated ESD protection which is typically very weak. Other strict EMI regulations and system requirements, as specified in GSM mobile phones, strongly request filters that reduce the radiated/conducted EMI. However, they must still comply with the electrical requirements of the interface specification.
The continuing trend of miniaturization of portable appliances implies that interface devices offering ESD protection and EMI filtering should also integrate biasing circuits/resistors into a single small-sized package. NXP’s memory card interface solutions fully support this continuing trend and offer interface conditioning functions such as high-level ESD protection according the IEC61000-4-2 standard. They also support EMI filtering, integrated biasing resistor networks, regulated power supply to supply SD-memory cards directly from a battery, and voltage level translation to enable the use of low-voltage host processors to communicate with 2.7 V to 3.6 V compliant SD-memory card devices.
Audio
Our digital audio amplifier family is built to simplify audio architecture by lowering the system cost and enabling easy interfacing. Using a digital interface eliminates the need for a D/A converter in the host processor, and the PDM or I2S format guarantees an ultra small IC footprint.
The digital interface assures low RF susceptibility in the device and the total system, and low sensitivity to input clock jitter. In addition, the digital interface eliminates the need for couple capacitors and safeguard speakers by eliminating problems coming from DC offsets due to leakage currents of an analog design.
Charger interface
Whether your device is charged via the USB port or a separate charger, it is exposed to incorrect polarity or abnormally high voltages. Any of these two occurrences poses a threat to the charger circuit and the PMU of the mobile device. In addition, the USB/charger port can be subject to ESD strikes and other transient discharges.
NXP offers an application specific portfolio of TVS diodes and ESD arrays, which enable cost efficient protection solutions – ESD, reverse polarity, overvoltage, other transient discharges – with the smallest footprint.
Diode & Transistors
• First leadless package with tin-plated side pads
For additional information, download guide
Download Full Block Diagram Below
Advertisement

Learn more about NXP Semiconductors





