Design Considerations
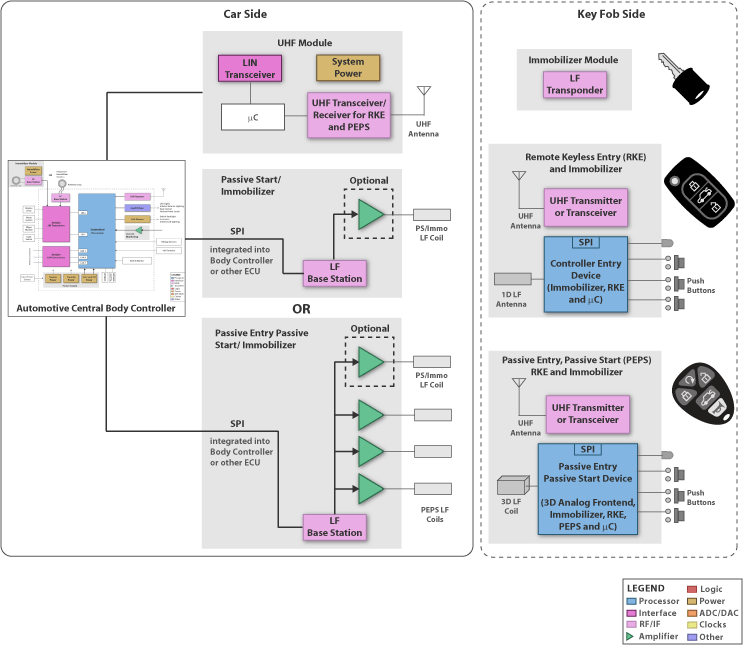
Very common car access functions are the immobilizer and the remote keyless entry system. For more advanced systems passive entry and passive start functions are implemented that allow unlocking or starting of the car by simply getting close to it.
TI RFID Automotive products offer market unique features and performance. All car side products are optimized for full integration into the Central Body Control Module (BCM). The Immobilizer LF antenna could be easily connected to the LF base station with a flexible cable length up to 13 feet (4m). The cable length could be varied without changing the adaptation to the base station. The integration of the base station reduces system component count and space requirements.
Immobilizer: The LF Immobilizer interface of all TI products works with a special half duplex transmission achieving market leading communication range resulting in flexible LF antenna placement at the key fob side and compact key fob design. TI offers compatible parts for the key fob from the transponder, over remote keyless entry controller to passive entry devices. All Immobilizer interfaces work without battery support on the key fob side.
Remote Keyless Entry: The Controller Entry Device manages the Immobilizer communication and push button interaction. During sleep state the devices enters a special low power mode with only 60nA current consumption. By pressing a push button the device wakes up and controls an external UHF transmitter or transceiver. Security keys and rolling codes could be stored in the integrated EEPROM memory. This memory is accessible over the LF interface without support from the battery in the key fob. The Controller Entry Device offers a special battery charge mode; to achieve faster charging it’s recommend to add a charging amplifier device on the base station side. The external resonant circuit with a LF coil and a resonant capacitor could be trimmed to the correct resonant frequency with the integrated trimming capability achieving an easy way to eliminate part tolerances.
Passive Entry: The Passive Entry Device manages the Immobilizer communication, push button interaction and LF wake reception. The special high Q design achieves communication ranges up to 3m for the passive entry link without outstanding low standby current on the receiver side. The front-end offers flexible configuration of 2 different wake patterns of 0, 4, 8 or 16 bit length. Each channel could be adjusted in sensitivity and resonance frequency which results in reproducible system designs. By pressing a push button the device wakes up and controls an external UHF transmitter or transceiver. Security keys and rolling codes could be stored in the integrated EEPROM memory. This memory is accessible over the LF interface without support from the battery in the keyfob. The Passive Entry Device offers a special battery backup mode to operate the microcontroller without battery support. The external resonant circuit with a LF coil and a resonant capacitor could be trimmed to the correct resonant frequency with the integrated trimming capability achieving a easy way to eliminate part tolerances.
UHF Transceiver/Transmitter/Receiver: Pin-to-pin and software compatible devices are available offering a easy way of scalability from standard one way communication to high-end bi-directional communication. The UHF device family comes with an easy to use SPI interface where all parameters of a UHF link could be configured. All building blocks of a UHF system are integrated in the devices requiring only one external oscillator, a matching network and the UHF antenna itself. The receiver and transceiver comes with a integrated polling mode (wake on radio).
Power management: The power supply is connected to the 12V or 24V board net and regulates down/up to voltages for DSP, uC, memory and ICs and functions DVD drive, communication interfaces, display biasing and back lighting. The need for many different power rails makes the design of the power supply a critical task when trying to design for size, cost and efficiency. Linear regulators with low quiescent current help reduce battery leakage current during standby operating modes (ignition off), are load dump voltage tolerant for directly battery connected devices, and need low drop out and tracking for low battery crank operation. Beyond providing increased conversion efficiencies, switching power supplies provide EMI improvement with slew rate control of the switching FET, Frequency hopping, spread spectrum or triangulation method for attenuation of peak spectral energy, Low Iq, soft start for power sequencing and in rush current limitation, Phased switching for multiple SMPS's regulators to minimize input ripple current and lower input capacitance, higher switching frequency for smaller components (L and C's), and SVS functions for brown out indications.
Communication interfaces: Allow data exchange between independent electronic modules in the car as well as the remote sub modules of the BCM and RFID system. High Speed CAN (up to 1Mbps, ISO 119898) is a two wire, fault tolerant differential bus. With a wide input common mode range and differential signal technology it serves as the main vehicle bus type for connecting the various electronic modules in the car with each other. LIN supports low speed (up to 20 kbps) single bus wire networks, primarily used to communicate with remote sub functions of the BCM system.
Click here for additional information
Download Full Block Diagram Below
Advertisement

Learn more about Texas Instruments





