Thermoelectric cooling and thermostating systems (TCTS) allow to maintain the set temperature of the object at the level of both above and below the ambient temperature.
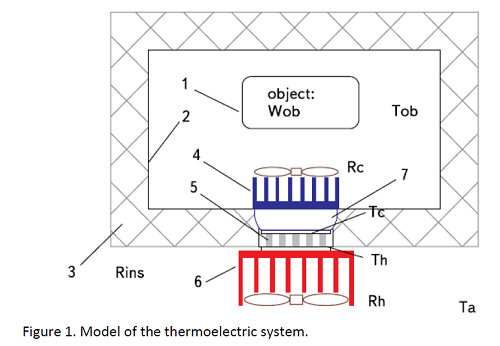
Any thermoelectric system can be divided into three main parts: the thermoelectric module itself and its cold and hot sides. However, there is a bit more things you need to know to build the proper thermoelectric system. For your convenience, we created a schematic image of the system to describe all the details.
The cold side includes a thermostatted object 1 at temperature Tob and with the heat output Wob, placed in the chamber 2.
The chamber is surrounded by thermal insulation 3 with thermal resistance Rins. Heat from the object by means of heat exchange 4 is transferred to the cold side of the thermoelectric module 5. The heat exchanger is usually a plate radiator cooled by blowing fan.
Heat removal from the hot side of the thermoelectric module is carried out by means of a hot heat exchanger 6. For transferring of heat through the layer of thermal insulation the heat conductor 7 is used. It is installed between the cold side of the module and the cold heat exchanger. The heat-conducting paste is applied, for example, KPT-8, to reduce the contact thermal resistance between the sides of the module and the surfaces of the heat exchanger.
Source: Ecogen Technology
Advertisement
Learn more about Electronic Products Magazine





