By Gina Roos, editor-in-chief
A new white paper released by the the Industrial Internet Consortium (IIC) offers a best practices roadmap to developing and deploying industrial internet of things (IIoT) solutions. The best practices are based on results from a compilation of nearly 30 IIC testbeds .
The white paper, “A Compilation of Testbed Results: Toward Best Practices for Developing and Deploying IIoT Solutions ,” covers lessons learned about project initiation, planning and management, establishing the value of platforms, dealing with brownfield constraints or limited resources, deploying supportive technologies such as machine learning and AI, and mistakes to avoid.
Although the IIC testbeds are different, they face the same challenges and share a lot in common with proof-of-concept and pilot projects. Testbed learnings, called horizontal learnings by IIC, provide insights on how to deploy IIoT and use emerging technologies such as AI and digital twins.
IIC covers horizontal challenges shared by many testbeds, including:
- Project initiation — approaching management for funding an IIoT project
- IT/OT mismatch — dealing with the cultural and human differences in information technology (IT) versus operational technology (OT)
- Human factors — including managing people’s concerns about IIoT pilot/project risks and fears about job relevance
- Other typical roadblocks — determining the IIoT technologies appropriate for the deployment context, dealing with limited resources and an uncertain timeline, disruptive trials in the production environment, integrating a diverse set of technologies and standards, and developing analytics models without a large quantity of data
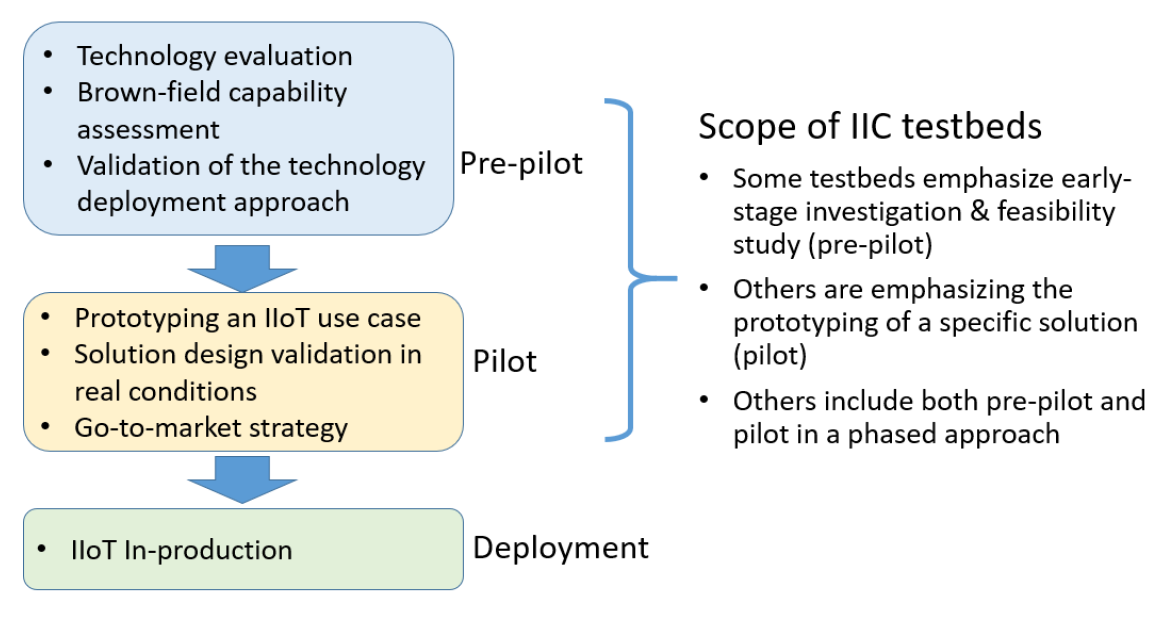
The scope of IIC testbeds
Analysis of the testbeds found four key mistakes that should be avoided. These include:
- Not spending enough time with the end user early on: Results indicate that many pilot projects don’t go beyond the successful demonstration phase if they don’t address long-term operational expectations and hidden restraints.
- Treating the end user just as a customer and not as a partner: It’s all about building a solution together with the end user, said IIC. Users should understand their role in the success or failure of the solution. Customers have key knowledge of their operations, an understanding of what can be done or should be avoided, and the expertise to judge a solution’s value, which should be leveraged, in developing a new IoT solution.
- Committing too early to objectives or business benefits: Overcommitting with insufficient knowledge of the operational context risks will disappoint everyone in the case of failure. When there are too many unknown variables in a new project, the best course of action, cited by the report, is to plan for an investigative phase and add a pre-pilot phase to understand the field conditions, clarify the best way to proceed, and define reasonable expectations.
- Keeping the objectives vague and success criteria imprecise: A lack of clear criteria for evaluating success increases the risks of misunderstanding the goals and expectations from the stakeholders. IIC advises that clear criteria should be defined and agreed upon by all stakeholders, phase by phase, so everyone is on the same page for phase goals and measurements.
The white paper provides more details on key approaches to avoid and implement when developing new IIoT solutions. IIC testbeds are where the use of new technologies, applications, products, services, processes, and business models can be initiated and tested to determine their viability before coming to market.
Advertisement
Learn more about Electronic Products Magazine





