By Warren Miller, contributing writer
Artificial intelligence (AI) is the next great technological frontier. If you’re doubtful, just look at all of the tech companies, big and small, devoting resources toward researching and developing AI. Google even developed its own AI chip a few years ago, called a tensor processing unit, or TPU for short. Now, in what could be a momentous event in the future of AI development, Google is making those processors available for purchase through its cloud-computing service.
You may be asking yourself why an internet-based company would be fabricating its own hardware in the first place. The truth is that Google has been developing and building hardware like servers and networking tools for years; it’s simply more cost-effective than purchasing similar hardware from a third party. Other internet and software giants, such as Amazon and Microsoft, build their own hardware, too.
Up until now, Google’s AI tech has been primarily focused on digital image recognition, a technology that many believe holds the key to the future of self-driving vehicles. The faster and more accurately an AI system can identify other vehicles, obstructions, or pedestrians, the safer that driverless cars will be. Late last year, the ride-sharing company Lyft began testing Google’s latest-generation TPUs in its own driverless vehicles, trying to accelerate the “learning process” for those AI systems. “There is huge potential here,” Anantha Kancherla, head of software development for Lyft’s self-driving vehicle project, told The New York Times.
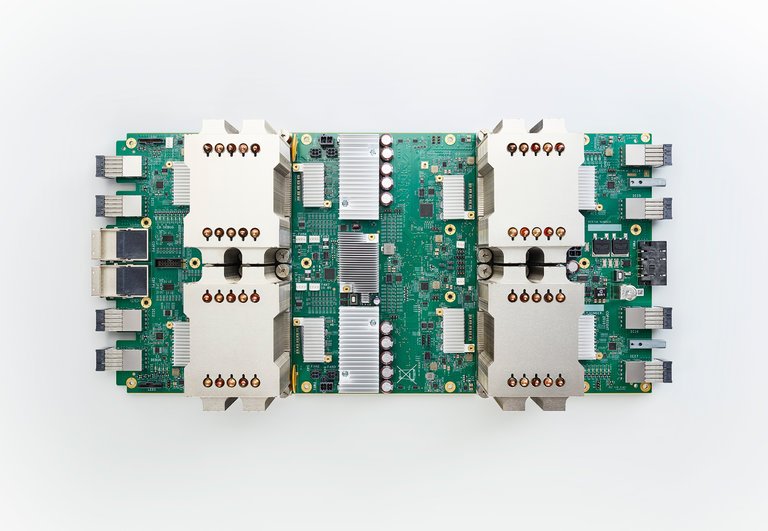
One of Google’s tensor processing units. Image source: Google.
By allowing other companies to incorporate TPUs into varying technologies, Google hopes to expand the many realms into which they can already be applied. TPUs have already been instrumental in accelerating the development of everything from Google Translate to Google Assistant, the voice-recognition app commonly found on Android phones. AI-based applications like Google Assistant employ intricate algorithms called neural networks to “learn” by evaluating enormous amounts of raw data. Google’s TPUs make “training” these algorithms much faster and more efficient, which the company hopes will give the entire AI-development field a stiff wind to propel the worldwide voyage of technological discovery.
Could the Google TPU become the processor of choice, much like the way that the ARM processor has become ubiquitous in the MCU arena? ARM seems to have won its place as the go-to processor by helping to create a deep and wide ecosystem of tools and supporting technologies that provide significant value over and above the raw hardware. The vast majority of this ecosystem was developed by other companies. Can Google manage to do something similar, or do they have a different playbook in mind?
It doesn’t seem like so long ago that artificial intelligence was the stuff of science fiction, like time travel or interstellar teleportation. Now that the world’s biggest tech companies are investing in not only developing AI tech of their own but allowing and encouraging the proliferation of that tech so that others can develop their own AI systems, the future may be right around the corner.
Advertisement
Learn more about Electronic Products Magazine





