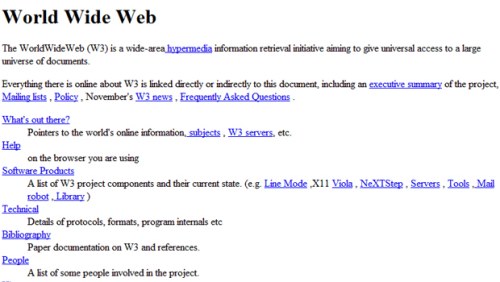
This is what the first website looked like 20 years ago.
The World Wide Web was created by British physicist, Tim Berners-Lee in 1989 at The European Organization for Nuclear Research (CERN), but did not hit the public domain until 1993.
According to CERN, by making this technology available on a royalty free basis, “the web was allowed to flourish.”
Initially, the World Wide Web was created for the purpose of sharing information between physicists around the world. The first website was hosted on Tim Berners-Lee’s NeXT computer. The website described features of the web such as how to access documents and set up a server.
Although the website is no longer available online at its original address, CERN started a project to restore the website in honor of its 20-year anniversary. Click here to browse the very first website.
The images below are copies of the documents that put the World Wide Web into the public domain on April 30, 1993.

Images via CERN.
Advertisement
Learn more about Electronic Products Magazine





