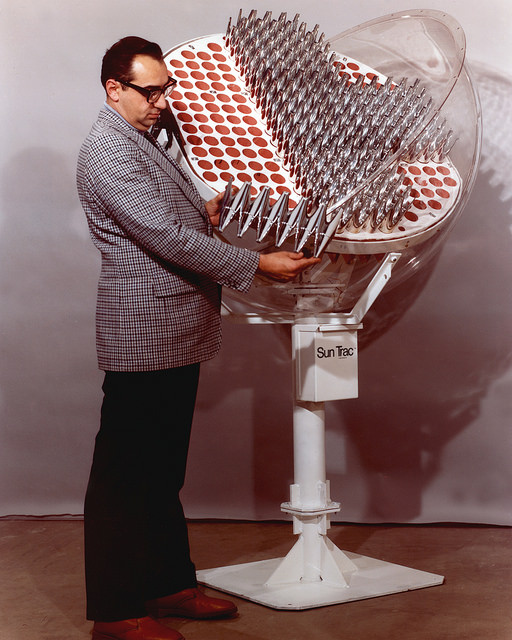
As per a request made by the Argonne National Laboratory in the 1970s, the device seen above was designed by Sun Trac Corporation for the purpose of photovoltaic conversion
Technically speaking, the image is a dual-axis array of non-imaging solar concentrators.
In layman’s terms, it’s an early version of today’s solar panels.

When the request was made, the lab was studying solar power and searching for more effective / efficient means of turning sunlight into electricity. The folks at Sun Trac made the decision to go with the unique shape you see in the photos because it allowed the solar concentrators to gather more sunlight, including that which might be scattered by haze, smog, and air pollution.
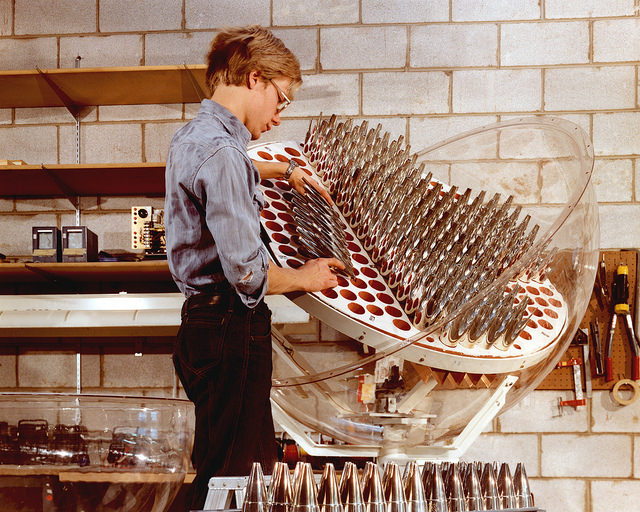
Worth noting is the fact that the concentrating reflectors used are multi-purposeful: they could also be used for solar heating and cooling systems, or with photovoltaic cells to convert sunlight into electricity.
Advertisement
Learn more about Electronic Products Magazine





