You don’t have to be a basement dwelling loony to feel compelled to extend the Wi-Fi range throughout your home. From the drastic jump in video streaming mobile devices to the number of Wi-Fi connected IoT devices, wireless range has become a top priority. But setting up a robust network doesn’t have to be daunting; just follow the practical tips below to establish Wi-Fi across an entire property.
Stick with a single SSID to speed up set-up and avoid headaches
Programming each single device with your network’s password is inconvenient enough as it is, so do yourself a favor, and use a single SSID (service set identifier) across all your wireless access points. Best case scenario, you simply input it on each one. Worst case scenario, the wireless range extender you have requires a different SSID than the one it’s repeating. If that’s the case, it may be worth investing in wireless range extenders that operate using Ethernet over the power line rather than repeating the incoming wireless signal.
Note that there is an important exception to this rule. If in addition to a 5 GHz network, you require a 2.4 GHz network to accommodate your older devices, then you may wish to give them differing SSIDs for two reasons. First, older IoT devices sometimes require connecting to a 2.4 GHz AP to configure them. Second, devices will often latch on to the 2.4 GHz when moving between multiple apps, when you’d rather them attach to the faster 5 GHz network.
Pay close attention to your channels and measure coverage to optimize speed
Each Wi-Fi band has a limited number of channels and most access points and routers allow you to select which channel to use, rather than settling for automatic setup. While there’s no perfect way to manually allocate channels, using a Wi-Fi analyzing mobile app helps you track which device uses which channel, and to what extent they’re overlapping and causing interference. Since interference results in bandwidth loss, it’s in your best interest to walk around the house tracking signal strength with the Wi-Fi analyzing app, and place signal repeaters in areas showing the highest signal strength.
Fewer overall units result in a better network
When it comes to Wi-Fi signal extension, having fewer, more powerful handoff devices results in higher performance than multiple underpowered ones. At the same time, regardless of the quality and number of devices, signal strengths drops off around the periphery of the range.
Until very recently, it was more economical to extend Wi-Fi range over a large area using discount routers set up as access points. There are now multiple purpose-built solutions, which we’ll cover below.
News mesh solutions offer improved performance over a patchwork network solution
Before new “mesh” technology hit the market, consumers were forced to extend range using a Rube Goldstein tangles of routers, access points, and repeaters. Now, the very same mesh technology available in the corporate world is also available for home use.
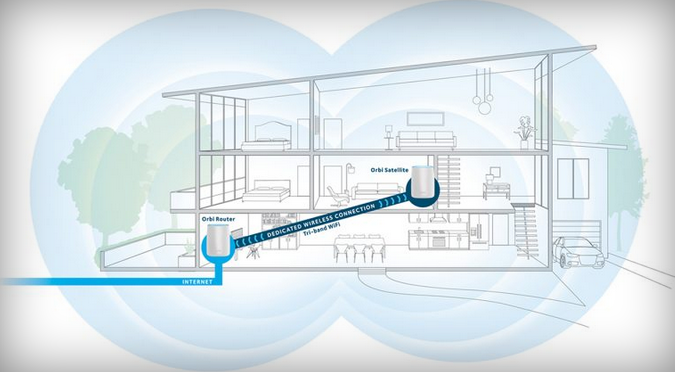
Instead of opting for the original Ubiquiti/Unifi device, which lacks user-friendliness, consider consumer-focused mesh network products like the Eero and Luma. If you prefer bigger names, pick up a solution from Netgear, Orbi, or even Google, which launched its own Wi-Fi home automation-friendly router.
Mesh-enabled solutions are expensive, but they’re the easiest way to go, handling SSID assignment, channel allocation, and management from a single interface. Some rely on mobile apps while others let you use a web interface. Whatever the case, mesh hardware tends to have improved online update capabilities, allowing for faster bug and security patching.
Source: ExtremeTech
6,280, – 13057
Advertisement
Learn more about Electronic Products Magazine





