Researchers from Nokia and scientists from the University of Southampton have published a proof-of-concept report that details how they were able to harness lightning and use its power to charge their personal devices.

This incredible breakthrough could open the door to one day seeing the use of nature’s most significant energy sources actually charge consumer electronics in a sustainable manner.
Now, while you might envision a scientist in a lab coat standing amid a torrential rainstorm, holding his smartphone to the sky, the entire experiment took place in a lab setting, where a Nokia Lumia 925 was used with an energy simulation that generated the power and effects associated with a typical bolt of lightning.
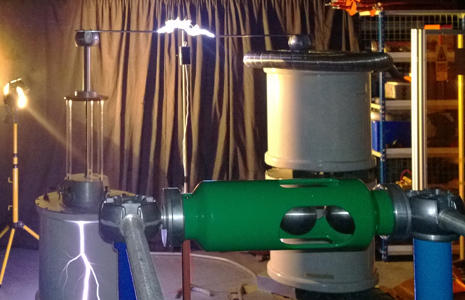
“We were excited by this challenge presented to us by Nokia,” explained scientist Neil Palmer of the University's Tony Davies High Voltage Laboratory. “Using an alternating current driven by a transformer, over 200,000 volts was sent across a 300-mm gap — giving heat and light similar to that of a lightning bolt. The signal was then stepped into a second controlling transformer, allowing us to charge the phone.”

“We were amazed to see that the Nokia circuitry somehow stabilized the noisy signal, allowing the battery to be charged. This discovery proves devices can be charged with a current that passes through the air, and is a huge step towards understanding a natural power like lightning and harnessing its energy,” he added.
See the experiment in action via the video below:
Full report (free): arxiv.org
Story via southampton.ac.uk
Advertisement
Learn more about Electronic Products Magazine





