Randy.Pinkelman@vishay.com
What is a resistor?
The resistor is the most common and well-known of the passive electrical components. A resistor resists or limits the flow of electric current in a circuit. There are many uses for resistors: they are used to drop voltage, limit current, attenuate signals, act as heaters, act as fuses, furnish electrical loads, and divide voltages. This tutorial provides an in-depth guide to the types of fixed resistors, their key specifications, and different fixed-resistor technologies.
Resistor symbol (U.S. and Japan).

Resistor symbol (Europe)
What is Ohm’s law?
Ohm’s law is a simple equation that shows the relationship between resistance, voltage and current through a metal wire, or some other type of resistive material. In mathematical terms, Ohm’s law is written as:
I = V/R ,
where I is the current in amperes, V is the voltage in volts, and R is the resistance in ohms.
Ohm’s law can also show the relationship between resistance, voltage, and power using the following equation:
P = V2 /R ,
where P is the power in watts, V is the voltage in volts, and R is the resistance in ohms.

Types of resistors
Fixed resistors. A fixed resistor is one in which the value of its resistance cannot change.
Variable resistors. A variable resistor is a resistor whose value can be adjusted by turning a shaft or sliding a control. They are also called potentiometers or rheostats and allow the resistance of the device to be altered by hand.
Nonlinear resistors. A nonlinear resistor is a resistor that has resistances that vary significantly with applied voltage, temperature or light. Types of nonlinear resistors are varistors, thermistors, and photoresistors.
Common resistor terminology
Critical resistance value. The maximum nominal resistance value at which the rated power can be loaded without exceeding the maximum working voltage. The rated voltage is equal to the maximum working voltage in the critical resistance value.
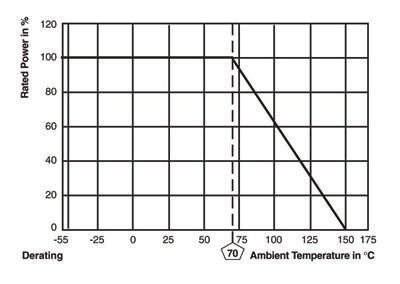
Derating curve. The curve that expresses the relation between the ambient temperature and the maximum value of continuously loadable power at its temperature, which is generally expressed as a percentage.
Dielectric withstanding voltage. The rated voltage that can be applied to a designated point between the resistive element and the outer coating, or the resistive element and the mounting surface, without causing dielectric breakdown.
Maximum overload voltage. The maximum value of voltage capable of being applied to resistors for a short period of time in the overload test. Typically the applied voltage in the short time overload test is 2.5 times larger than the rated voltage. However, it should not exceed the maximum overload voltage.
Maximum working voltage (or maximum limiting element voltage). The maximum value of DC voltage or AC voltage (rms) capable of being applied continuously to resistors or element. However, the maximum value of the applicable voltage is the rated voltage at the critical resistance value or lower.
Noise. Noise is an unwanted AC signal from within the resistor. Resistive noise can have a devastating effect on low-level signals, charge amplifiers, high gain amplifiers, and other applications sensitive to noise. The best approach is to use resistor types with low or minimal noise in applications that are sensitive to noise.
Power rating . Power ratings are based on physical size, allowable change in resistance over life, thermal conductivity of materials, insulating and resistive materials, and ambient operating conditions. For best results, employ the largest physical size resistors at less than their maximum rated temperature and power.
Rated ambient temperature . The maximum ambient temperature at which resistors are capable of being used continuously with the prescribed rated power. The rated ambient temperature refers to the temperature around the resistors inside the equipment, not to the air temperature outside the equipment.
Common resistor terminology
Rated power . The maximum amount of power that can be continuously loaded to a resistor at a rated ambient temperature. Network and array products have both rated power per package as well as per element.
Rated voltage . The maximum value of dc voltage or AC voltage (rms) capable of being applied continuously to resistors at the rated ambient temperature.
Reliability. Reliability is the probability that a resistor (or any other device) will perform its desired function. There are two ways of defining reliability. One is Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF) and the other is Failure Rate per 1,000 hours of operation. Both of these means of evaluating reliability must be determined with a specific group of tests and a definition of what is the end of life for a device, such as a maximum change in resistance or a catastrophic failure (short or open). Various statistical studies are used to arrive at these failure rates and large samples are tested at the maximum rated temperature with rated load for up to 10 000 hours (24 hours per day for approximately 13 months). Reliability is generally higher at lower power levels.
Resistor tolerance . Resistor tolerance is expressed as the deviation from nominal value in percent and is measured at 25C only with no appreciable power applied. A resistor’s value will also change with applied voltage (VCR) and temperature (TCR). For networks, absolute resistor tolerance refers to the overall tolerance of the network. Ratio tolerance refers to the relationship of each resistor to the others in the package.
Stability. Stability is the change in resistance with time at a specific load, humidity level, stress, or ambient temperature. When these stresses are minimized, the better the stability.
Temperature coefficient of resistance (TCR also known as RTC) . TCR is expressed as the change in resistance in ppm (0.0001%) with each degree Celsius of change in temperature. TCR is typically referenced at 25C and changes as the temperature increases (or decreases). A resistor with a TCR of 100 ppm/°C will change 0.1% over a 10°C change and 1% over a 100°C change. In the context of a resistor network, the TCR value is called the absolute TCR in that it defines the TCR of a specific resistor element. The term “TCR tracking” refers to the difference in TCR between each specific resistor in a network.
Temperature rating. Temperature rating is the maximum allowable temperature at which the resistor may be used. It is generally defined with two temperatures. For example, a resistor may be rated at full load up to 70 °C derated to no load at 125 °C. This means that with certain allowable changes in resistance over the life of the resistor, it may be operated at 70 °C at rated power. It also may be operated with temperatures in excess of 70 °C if the load is reduced, but in no case should the temperature exceed the design temperature of 125C with a combination of ambient temperature and self-heating due to the applied load.
Voltage coefficient of resistance (VCR) . The voltage coefficient is the change in resistance with applied voltage. This is entirely different and in addition to the effects of self-heating when power is applied. A resistor with a VCR of 100 ppm/V will change 0.1% over a 10 V change and 1% over a 100 V change. In the context of a resistor network, this VCR value is called the absolute VCR in that it defines the VCR of a specific resistor element. The term VCR tracking refers to the difference in VCR between each specific resistor in a network
Surface mount / substrates / wirebondable resistors
Axial leaded / through-hole resistors
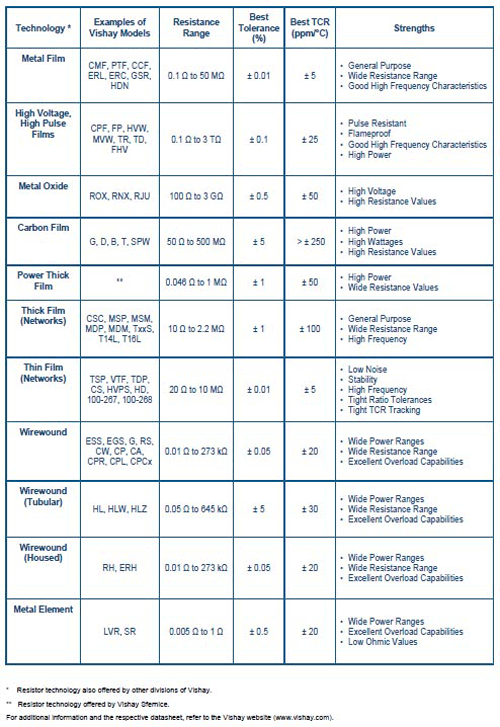
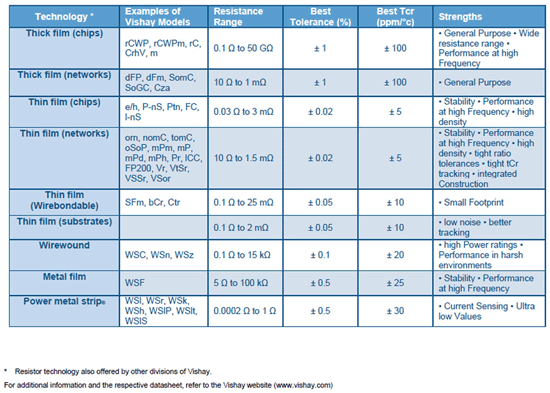
Fixed-resistor technologies

Wirewound (surface-mount / leaded) . a type of resistor made from winding a metal wire, such as nichrome, on an insulating form, such as a ceramic, plastic, or fiberglass core.
Power Metal Strip / metal element (surface-mount / leaded) . A type of resistor constructed using a solid metal alloy, such as nichrome or manganese-copper, as the resistive element, which is then welded to copper terminals. Used in current sense and shunt applications.
Film (surface-mount / leaded), Metal film (Leaded/meLf) . A type of cylindrical resistors made by depositing a resistive element made of a thin conducting film of a metal or metal alloy, such as nichrome, onto a cylindrical ceramic or glass core. the resistance is controlled by cutting a helical groove through the conducting film.
Metal oxide (leaded) . A type of cylindrical resistor that uses materials such as ruthenium oxide or tin oxide as the resistive element. these resistors can be excellent high-voltage or high-power devices.
Thick film (chip resistors/chip arrays/networks) . Specially built surface-mount film resistor that carries high power for the part size. For thick film resistors, the ruthenium oxide “film” is applied using traditional screen-printing technology.
Thin film (chip resistors/chip Arrays/networks). A type of surface-mount film resistor with a relatively thin resistive element, measured in angstroms (millionths of an inch). thin film resistors are made by sputtering (also known as vacuum deposition) a resistive material, such as nichrome or tantalum nitride, onto the surface of a substrate.
Carbon film (Leaded/meLf) . A general class description for cylindrical resistors made by depositing a carbon film on the surface of a center core insulator.
Composition (leaded)
Carbon composition. A general class description for resistors consisting of a carbon mixture resistive core and a molded outer insulating core.
Ceramic composition . A type of resistor that consists of a clay, alumina, and carbon mixture that has been blended and pressurized into a resistive core and then covered with a molded outer insulating core.
Advertisement
Learn more about Vishay Dale





