Energy efficiency, functionality, reliabilityand cost toocreate a compelling case for changing to solid-state lighting
BY ROLAND CHAPA
OPTEK Technology
Carrollton, TX
http://www.optekinc.com
From the slot machines in Las Vegas and Atlantic City to the pinball and skee-ball machines in local arcades, gaming machines are constantly running. These brightly lit machines stay on 24 hours per day, consuming an incredible amount of power. At the same time, reliability is paramount if these not-inexpensive machines are to generate the most revenue possible,

LEDs are being integrated into slot machines for both high energy efficiency and cost savings. (Photo © iStockphoto.com/Stefan Klein)
LEDs now compete with incandescent and fluorescent lights as illumination options for gaming machines as well as other applications. By considering such factors as energy efficiency, functionality, reliability, and cost savings, designers can select the most appropriate light source suited for these applications.
Energy efficiency
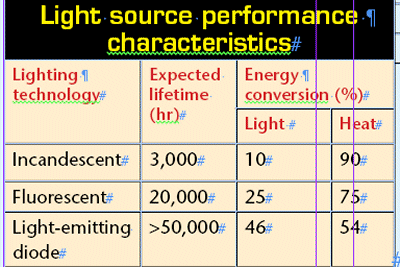
Long used to backlight the bright signage of slot machines and other casino gaming systems, incandescent and fluorescent bulbs can use a significant amount of energy and in the process generate a considerable amount of heat, which often results in bulb failure and machine down-time for replacement (see table ).
With a high flux output and low thermal resistance, an LED converts only 54% of supplied energy to heat, as compared to 90% conversion for an incandescent bulb.
Because a single slot machine can consume up to 1 kW of energy per day, the conversion to LEDs represents a substantial energy savings, particularly if you take into account the growth in the gaming industry over the last several years and the number of machines in major gaming cities like Las Vegas and Atlantic City.
Cutting back on the heat generated by lighting sources produces further energy savings by reducing the need to run fans, air conditioning, and other cooling systems.
Functionality
In addition to illumination, light sources can provide special functionality to gaming systems. Due to their small size and high efficiency, LEDs generally provide more flexibility and functionality than fluorescent and incandescent bulbs.
An incandescent or fluorescent bulb radiates light over 360º and thus requires a reflector to shift the light back into a concentrated area, providing somewhat limited lighting effects. An LED can be controlled without reflectors, through placement of the LED itself as well as specialized lensing.
By their nature LEDs can, in fact, work well with a variety of different lens configurations and secondary optics. As a result, they are well equipped to direct and diffuse light, as well as create different shapes and patterns. Thus LEDs are well suited for applications requiring a wider beam area, such as backlighting for large graphics, as well as for task lighting, and especially the small-area illumination required by gaming machines.
Having a variety of colors in arrays or trace patterns also provides increased functionality for gaming systems. The ability to produce a broad range of colors is key for producing the specific colors of a particular brand, and many gaming manufacturers have their logos prominently displayed on the machine.
Traditional light bulbs capable of meeting gaming requirements often come only in white, and thus require gels or filters to display different colors, making it very difficult to achieve the desired lighting effect. On the other hand, RGB-type LEDsdevices able to produce all three primary colors in a single unitcan be easily tuned to match a Pantone matching system (PMS) color or any color in the visible spectrum, without filters or extra lenses.
Either through a combination of an array of RGBs or by mounting many individual LEDs of various colors, a gaming machine designer can produce multiple colors or patterns that can be digitally controlled. Additionally, by putting several LEDs together in different configurations and packages to create an array, it is possible to provide a variety of colors for specific applications—fluorescent bulbs do not afford this capability.
“Moving” lights and “trace patterns” help draw people to a gaming machine and keep them involved with it, further contributing to profit, and are thus highly desirable. Such effects can be achieved with incandescent sources, but require considerable power and numerous electronic components, such as relays, to drive them. LED trace patterns readily lend themselves to digital control and do not require nearly as much power, for either color changes or to produce movement effects.
There are different ways to adjust the power output of an LED. This is particularly beneficial when adjusting light output for daylight and nighttime. Diagnostic capabilities are yet another benefit to the use of LEDs in entertainment electronics.
While it is also possible to adjust power output with incandescent bulbs, LEDs permit every color to be independently controlled for high output from each individual chip, contributing to the efficiency and in turn, cost savings.
farcoptek2_oct2007 In addition to reliability, LED devices like OPTEK Technology’s 1-W Lednium can provide unique functionality for gaming applications.
Cost and reliability
Currently, LEDs are initially more expensive than incandescent or fluorescent bulbs. But when it comes to total cost of ownership, LEDs are actually much less expensive.
The expected lifespan of an LED is greater than 50,000 hours, whereas the lifespan of a fluorescent lamp is only about 20,000 hours, and an incandescent’s life is only 3,000 hours, 6% that of an LED’s. The extended lifespan results in fewer replacementsan incandescent will have to be replaced 16 times before an LED needs attention.
The reliability of LEDs results in substantial long-term cost-savings. Further, it maximizes income in several ways. If a gaming machine is not running because it requires lighting maintenance, money is lost. By the same token, if the machine is running but the lights are out, people may think it is disabled and not play it.
While an ordinary light bulb’s life ends when it “goes out,” an LED’s end of life is defined as the point at which it degrades to 60% of its original output. In gaming machines applicationswhere lighting is paramount to economic productivityit’s better to have a light that dims over time rather than one that goes dark without warning. ■
For more information on LEDs visit www.electronicproducts.com/opto.asp
Advertisement
Learn more about TT electronics Optoelectronics Business Unit (OPTEK)





