Base station emulator supports WiMAX protocol conformance test (PCT)
BY MICHAEL LAWTON
Agilent Technologies UK
South Queensferry, West Lothian, U.K.
http://www.home.agilent.com/agilent/home.jspx?lc=eng&cc=GB
The WiMAX Forum is an industry body that promotes market adoption for technology developed in the IEEE 802.16 standards arena. This standards group has been very active in developing technology for high-speed wireless networks. Initially the focus was on replacing fixed infrastructure with high-speed wireless point-to-point solutions. In more recent times the standards efforts have focused on providing technology that will support mobile high-speed DSL-like Internet connections.
WiMAX technology and test
WiMAX technology addresses three primary market drivers, namely:
1. High speed wireless data throughput
2. Quality of service in an IP world
3. Mobile device convergence
High-speed wireless data throughput
An increased demand for data services has shifted the focus for designers developing wireless technologies. Early generations of cellular technology were designed to offer voice services with high spectral efficiency. These systems had defined bandwidth needs and hence would benefit little from temporary bursts of high bandwidth. For data, however, maximizing the throughput, for a given channel, provides a significant benefit. MIMO (multiple inputs, multiple outputs) technology exploits channel multipath to simultaneously transmit multiple data streams on the same frequency. MIMO therefore has the potential to provide spectral efficiency gains which can exceed the classical Shannon Hartley capacity limits! MIMO techniques rely on accurate channel estimation. OFDM (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing) is a modulation technique that divides the signal into many narrowly spaced carriers. The use of OFDM simplifies the MIMO channel estimation equations as the narrow frequency spacing allows each carrier to be modelled assuming narrowband fading channels. For these reasons the combination of MIMO and OFDM is very attractive for high-speed wireless data.
Quality of service in an IP world
WiMAX is one of the first wireless standards to be developed on the assumption that the communications world is dominated by IP (Internet Protocol), and it can be used to support all types of services. To address multiple service types the 802.16 standards group has developed the following quality of service category types:
• Best Effort (BE)
• Unsolicited Grant Service (UGS)
• Real-time Polling Service (rtPS)
• Extended real-time Polling Service (ertPS)
• Non real-time Polling Service (nrtPS)
A key factor of the performance of WiMAX technology is how well these QoS categories perform in the presence of multiple service flows on a congested wireless network.
Convergence
WiMAX technology is intended to be used in both the computing and communication devices. As a result it needs to develop solutions that support the use models and technologies used in both markets. This means supporting different security algorithms, intersystem handover, and idle mode to support voice as well as data services.
WiMAX forum validation process
The WiMAX Forum is developing a certification program for Mobile WiMAX technology. Achieving WiMAX certification is recognition that the equipment has successfully passed a defined set of tests and hence has a certain level of performance/inter-operability. The Mobile WiMAX certification program is divided down in to four areas:-
• Radio Conformance Test (RCT)
• Protocol Conformance Test (PCT)
• Mobile Inter-Operability Tests (mIOT)
• Radiated Performance Tests (RPT)
PCT and RCT are both conformance tests which require the use of purpose built test equipment. The WiMAX Forum operates a validation process whereby only equipment which has been “validated” can to be for conformance testing, as part of the certification process.

Fig. 1. A schematic representation of the validation process for the PCT.
The TSS&P (Test Suite Structure & Test Purposes) document references the PICS and provides text based description of the requirements and purpose for each of the protocol tests required. This is used by ETSI (European Telecommunications Standards Institute) as a definition for each of test cases. ETSI develop TTCN-3 code for each of the tests described in the TSS&TP. Finally, the WiMAX ATS (Abstract Test Suite) is an ETSI document which defines the architecture of the TTCN-3 system used for PCT testing. This document also defines variables used during the testing.
The goal of the validation process is to ensure that, using a given vendors implementation, the implementation of the ETSI test cases works in accordance with the test description in the TSS&TP. To do this, a validation lab has been established at AT4 in Malaga, Spain. There instrument vendors are working alongside equipment vendors to perform testing in preparation for validation.
For wave 1 Mobile WiMAX, the TTA (Telecommunications Technology Association, in Korea) has been selected as the organisation responsible for overseeing this testing. The requirements for a vendor achieving validated status are that their instrument must support all required test cases, that each test will pass on at least there different vendors’ mobile stations, and that the implementation will stand up-to scrutiny when compared with the TSS&TP. For PCT Agilent, Anite and AT4/Aeroflex are active members of the validation process and at the time of writing the validation process is still in progress.
WiMAX PCT
Figure 2 shows a schematic diagram for the Agilent N6430A WiMAX PCT test system. The architecture for the system is based around a TTCN-3 (Testing and Test Control Notation, version 3) test methodology. TTCN originally stood for Tree and Tabular Combined Notation and was developed as a language designed for testing digital systems. An earlier version of TTCN is used for protocol signalling conformance tests for 3G cellular technologies. TTCN-3 standardization has been led by ETSI and provides some significant benefits. In particular TTCN-3 provides a defined layer of abstraction between the TTCN-3 test environment and the hardware used to provide the “real world” test system. In theory this allows PCT users to develop TTCN-3 scripts, according to a TRI (TTCN-3 Run-time interface) interface, which will then be supported by each of the PCT hardware vendors, independent of their specific implementation.
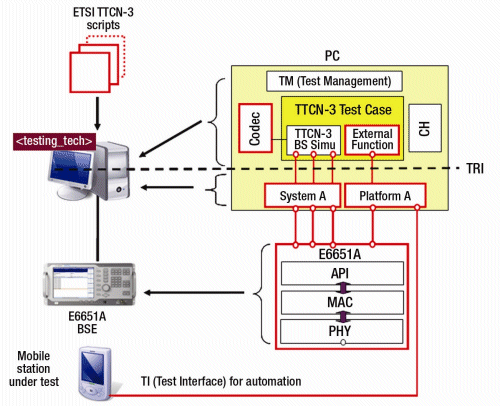
Fig. 2. As shown (in red,) the WiMAX specific elements of the PCT system architecture, are the TRI interface, the platform adaptors (PA) and system adaptors (SA), and codecCODEC.
The TRI interface defines the commands available within the TTCN-3 scripting environment. This interface consists of the definition of a number of ports, which are connected to the System Adaptor (SA). These ports allow the sending and receiving of WiMAX messages using standard commands defined within the ETSI TRI specification. In addition a series of WiMAX specific external functions are also defined and made available to the script developer. The external functions communicate with the platform adaptor and provide a means of both controlling the test system and providing a notion of time throughout the test system.
The system and platform adaptors are developed by the test vendor. These connect the TRI interface with the physical hardware and provide a mapping between the commands available at the TRI interface and the specific requirements of the hardware used in the system.
Finally the codec provides the software representation of the coding and decoding associated with the functionally of the digital system under test. In the case of PCT the codec is able to de-code and encode the required TLV (Type. Length, Value) commands supported by the 802.16-2004 cor2/d3 Mobile WiMAX Specification.
The TRI interface and codec information provides the necessary information to support the developer in writing TTCN-3 scripts for the purpose of Mobile WiMAX testing. Agilent offers focused solutions meeting the needs of both users wishing to perform conformance based testing using ETSI scripts, and those needing to develop scripts to support their own test coverage needs. ■
For more on products for mobile WiMAX, visit http://electronicproducts-com-develop.go-vip.net/linear.asp.
Advertisement
Learn more about Agilent Technologies





