Texas Instruments Inc. (TI) has launched two power-conversion device portfolios that deliver higher power density in smaller spaces. These new power devices include the 100-V integrated gallium nitride (GaN) power stages for mid-voltage power applications and the 1.5-W isolated DC/DC modules with integrated transformers for automotive and industrial applications.
The new power devices highlight TI’s focus on solving power design challenges. These include increasing power density, reducing electromagnetic interference (EMI), shrinking solution size, lowering cost and making systems safer.
“TI has a unique approach toward power density and how we are enabling smaller footprints, improving our packages and thermal performance, integrating a ton of features and adopting very innovative technologies so that we can deliver the power density and efficiency to the power designers,” said Rajarshi (Raji) Mukhopadhyay, TI’s product line manager of high-voltage controllers.
TI is working with power designers across a variety of market sectors to address each of these challenges that they are facing in tandem while understanding that the design cannot be optimized for only one of the requirements, Mukhopadhyay said. “We have to think through every angle so that we can optimize all the performance requirements that they have, including the system solution size, height and weight, as well as thermal performance, efficiency, noise, EMI and many others.”
Power density is a key differentiator for both portfolios, said David Snook, TI’s product line manager for GaN. The reason it is a focus at TI is that every new technology advancement demands more power in a smaller space and size is limited in power-supply design, he continued.
“Power-supply designers and engineers face constant pressure to do more with less, and while this trend isn’t new, it’s definitely not slowing down,” Snook said.
AI in enterprise data centers is one application that drives the trend for higher power density, Snook said. AI computing is based on hardware accelerators that consume much higher power than traditional compute servers, which means that server power supplies will need to provide much higher power within the same form factor to enable these future AI applications, he added.
These advancements in power density go hand in hand with development in other areas like improved efficiency and thermal management, as well as reducing overall system costs, Snook continued. “TI’s new power portfolios are enabling designers to address these challenges with small packages, higher power and fewer tradeoffs.”
Higher power density applies to many markets and applications, including industrial power applications, and one example is solar energy systems, which increasingly need smaller, more efficient power supplies, Snook said. For the solar inverter or the solar microinverters, higher density and efficiency enable the same solar panel to generate more power while decreasing the size of the overall system, he said.
In end equipment like this, this is where GaN has grown significantly due to its superior switching performance, Snook said.
100-V GaN power stages
The new 100-V GaN power stages, the LMG2100R044 and LMG3100R017 with thermally enhanced dual-side–cooled package technology, are designed to simplify thermal designs, reduce power-supply solution size and deliver high power density. Four target markets include solar energy, servers, telecommunications and industrial motor drives.
With the new 100-V GaN power stages, designers can reduce the power-supply solution size for mid-voltage power applications and achieve industry-leading power density of over 1.5 kW/in.3, which is enabled by GaN technology’s low switching losses and higher switching frequency, Snook said.
In addition, the integration of GaN FETs and gate driver into a single multi-chip package will shrink the required board area by over 40% compared with a discrete implementation while reducing the bill of materials and simplifying board layout, he added.

The 100-V integrated GaN power stages reduce PCB size by more than 40%. (Source: Texas Instruments Inc.)
Snook said there are three key factors that make the GaN power stages exciting for customers. The first is the reduction in switching power losses by 50% while achieving higher system efficiency of 98%, compared with 94% to 96% for silicon and discrete solutions and with 60% lower output capacitance and 50% lower gate-drive losses.
Secondly, the GaN power stages help reduce system costs with a simplified thermal design and by enabling a high switching frequency, Snook said. It also makes it easier for designers to meet their thermal design targets and reduce their overall system sizes.
The dual-side–cooled package technology enables more efficient heat removal from both sides of the device and offers improved thermal resistance compared with competing integrated GaN devices, according to TI. “The thermally enhanced top-side–cooled package with an extended bottom-side ground pad, effectively enabling dual-side cooling, is new for the 100-V power space,” Snook said. “It enables much more efficient heat removal in systems from both sides of the board, leading to 18× improved thermal resistance to the case compared with previously available packaging.
“The improvement in thermal dissipation is critical for systems without active cooling elements, such as telecom or solar inverters, which can now use much smaller heat sinks to dissipate the heat from the power-conversion system,” he added.
The other benefit of moving to GaN with high switching frequency, specifically enabled by the LMG2100 and LMG3100 series, is that engineers can use much smaller passives and, in isolated topologies, use a lower amount of transformer windings, which helps reduce overall system costs, he added.
The GaN power stages are optimized for common topologies, including buck converters, boost converters, buck-boost converters, LLC converters, PSFB, BLDC motor drives and Class D audio.
1.5-W isolated DC/DC modules
The new 1.5-W isolated DC/DC modules with integrated transformers, the UCC33420-Q1 and UCC33420, are claimed as the industry’s smallest and most power-dense, helping engineers shrink the isolated bias power-supply size in automotive and industrial systems by over 89%.
Electrification is a key sector, and powertrain and battery management system (BMS) designers are continuously seeking new ways to improve the system power density and efficiency, Mukhopadhyay said. Isolated bias supply solutions are an integral part of these systems, which provides the bias supply to the isolated secondary-side circuitry, he added.
“Typically, isolated bias supply solutions have traditionally required heavy, bulky external transformers that are prone to vibrations that increase the weight of the system and which overall complicate the design layout,” Mukhopadhyay explained. “External transformers also affect the performance efficiency and can lead to high radiated emissions.”
The new isolated DC/DC modules with integrated transformers built inside the package enable higher power density without having to design an external transformer, eliminating the challenges, he added.
“The breakthroughs in the transformer design have allowed us to integrate the transformer and silicon inside the same package, which reduces the overall power-supply height and size significantly,” Mukhopadhyay said.
Claiming over 8× higher power density than discrete solutions and 3× higher power density than competing modules, the DC/DC modules deliver the highest output power and isolation capability (3 kV) for automotive and industrial systems in a 4 × 5-mm, very thin, small-outline, no-lead (VSON) package.
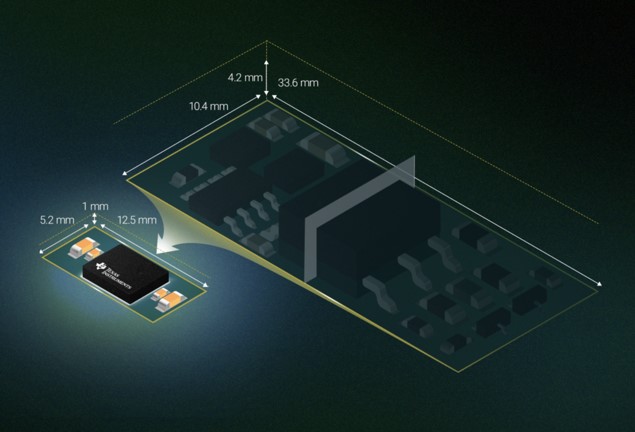
The smallest 1.5-W isolated DC/DC modules offer over 8× higher power density than discrete solutions. (Source: Texas Instruments Inc.)
The new modules use TI’s next-generation integrated transformer technology, which eliminates the need for an external transformer in a bias supply design. In addition to reducing the solution size by more than 89%, it reduces height by up to 75% and the bill of materials by half compared with discrete solutions, thanks to the high integration.
This first automotive-qualified solution in this small package can reduce the footprint, weight and height of the bias supply solution for electric-vehicle systems. For space-constrained industrial power delivery in data centers, the new module enables designers to minimize printed-circuit–board area, TI said.
“The UCC33420-Q1 part number is the first automotive-qualified 1.5-V isolated DC/DC module in this smallest package in the market, and that enables the designers to meet their demands for smaller, lighter and less noisy automotive systems, such as traction inverters, on-board chargers and battery management systems,” Mukhopadhyay said.
In addition, with ultra-low EMI, the DC/DC modules enable designers to meet stringent EMI requirements, such as Comité International Spécial des Perturbations Radioélectriques (CISPR) 32 and 25, with fewer components and a simple filter design. They also withstand extremely high-voltage transients with the industry’s highest common-mode transient immunity (CMTI) of >200 V/ns and less than 3-pF primary-to-secondary capacitance.
Mukhopadhyay said the three key benefits that the DC/DC modules bring are the integrated transformer technology, EMI optimization and low noise.
The UCC33420-Q1 integrates an isolation power transformer, primary- and secondary-side bridges and control logic into one package, which enables designers to eliminate the need for external bulky transformers, and it integrates a lot of features inside the package to reduce the overall system size, he said.
The second piece is that this transformer embedded inside the package is EMI-optimized, which makes it less noisy and enables the designers to meet the most stringent industry EMI standards like CISPR 32 and CISPR 25 Class 5, Mukhopadhyay said. This translates into fewer external components required and a simpler and lower-cost EMI filter design on the board.
“Thirdly, designers can concurrently achieve the most robust solution against noise,” he said.
The embedded transformers with very low primary- to secondary-side–coupling capacitance, less than 3 pF, enables the DC/DC modules to withstand very high CMTI, up to 200 V/ns, so the devices can withstand the noise in a noisy environment, he continued.
Production quantities of the LMG2100R044 and LMG3100R017 100-V GaN power stages are available for purchase on TI.com. The LMG2100R04 is available in a 5.5 × 4.5-mm, 16-pin quad-flat no-lead (QFN) package, and the LMG3100R017 is available in a 6.5 × 4.0-mm, 16-pin QFN package. Pricing starts at $3.75 in quantities of 1,000. Evaluation modules, LMG2100EVM-078 and LMG3100EVM-089, are available. TI also offers two reference designs: the 1.6-kW GaN-based bidirectional microinverter reference design and the 400-W GaN-based MPPT charge controller and power optimizer reference design.
Preproduction quantities of the UCC33420 and UCC33420-Q1 1.5-W isolated DC/DC modules are available for purchase on TI.com. Pricing for the UCC33420 and UCC33420-Q1 devices, housed in a 4 × 5-mm, 12-pin VSON package, starts at $1.30 in quantities of 1,000. Other versions of these devices with lower input voltages, output voltages and power ratings are expected to be available in the second quarter of 2024. Additional package options for 800-V and higher applications will also be available. An evaluation module, UCC33420EVM-080, is available now.
These devices will be on display at APEC 2024, Feb. 25–29, at TI’s booth 1145. TI will showcase its latest automotive and industrial designs, including 48-V automotive power; the first USB Power Delivery Extended Power Range full-charging solution on the market; an 800-V, 300-kW silicon carbide–based traction inverter; and high-efficiency power for server motherboards. TI will also participate in 20 industry and technical sessions to address power-management design challenges.
Advertisement
Learn more about Texas Instruments





