By Gina Roos, editor-in-chief
Rapid innovation in virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) products will take place only with the right components that help bring a more immersive experience, providing the processing and imaging capabilities required, while reducing power consumption. Many of these devices are also housed in smaller packaging or offer high integration for these space-constrained products. Here are 10 components that are designed with VR/AR applications in mind.
1. Vishay Intertechnology VCNL36687S proximity sensor
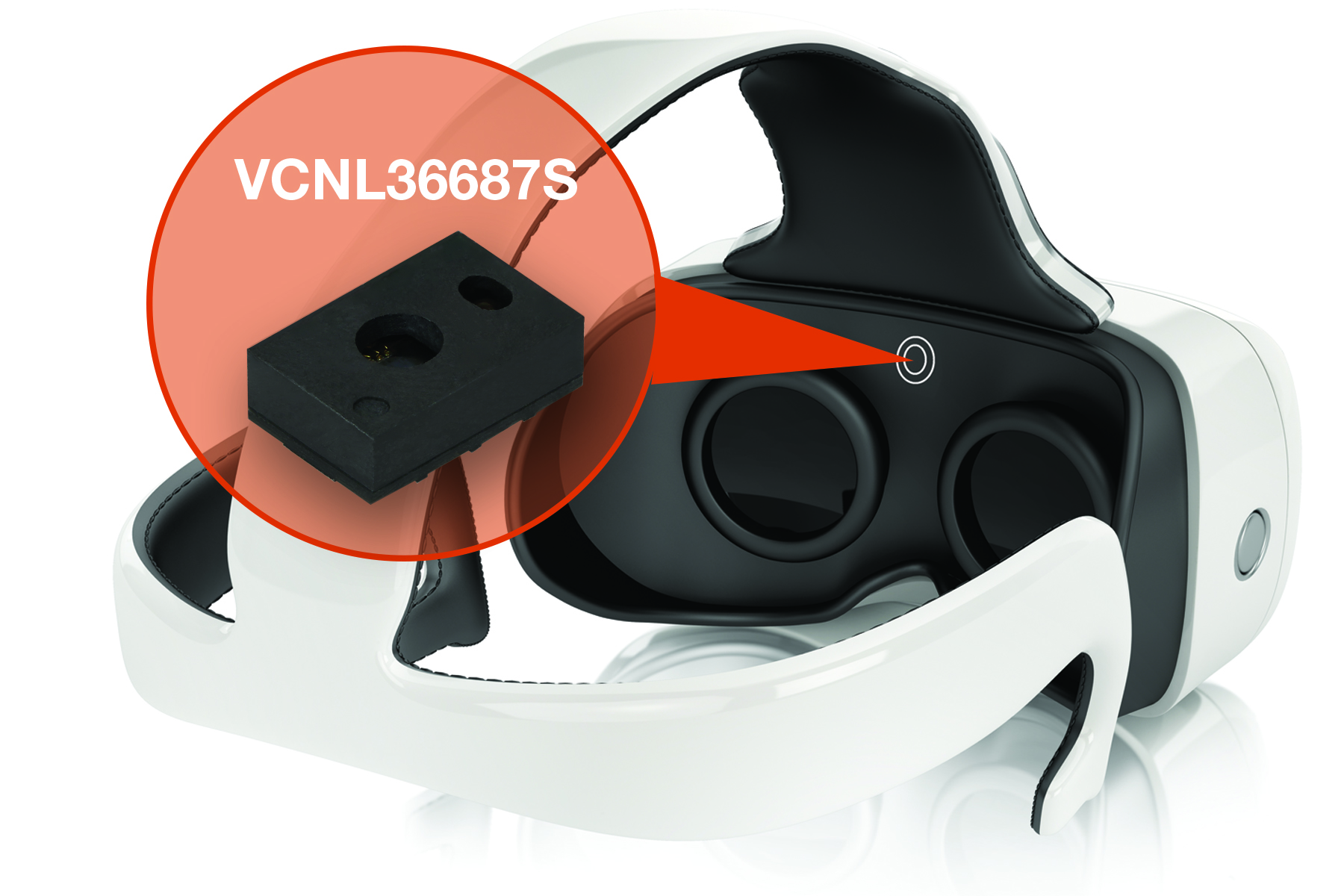

Vishay introduced a fully integrated proximity sensor that combines a high-power vertical-cavity surface-emitting laser (VCSEL), a photodiode, a signal processing IC, and a 12-bit ADC in a single package. The VCNL36687S is designed for smartphones, tablets, VR/AR headsets, and other battery-operated devices.
The VCNL36687S offers a range of up to 20 cm (7.9 inches), and the VCSEL’s profile of ±3° makes it suitable for applications that require narrow-angle detection while minimizing optical system design concerns. In terms of size, the VCNL36687S is housed in a miniature, surface-mount 3.05 × 2-mm leadless package (LLP) with a 1-mm profile, making it suited for space-constrained applications.
Vishay also improved the power consumption compared to previous-generation devices. As an example, the VCNL36687S can detect a Kodak Gray Card at a distance of 20 cm with a 20-mA pulse current, compared to 200 mA of current for previous VCNL series devices.
The VCNL36687S allows access to the proximity signal through a standard I2 C bus serial digital interface. The device’s programmable interrupt function provides wake-up functionality for the microcontroller when a proximity change occurs. This reduces processing overhead by eliminating the need for continuous polling, said Vishay.
2. TDK/Chirp Microsystems SonicTrack 6-DoF ultrasonic controller
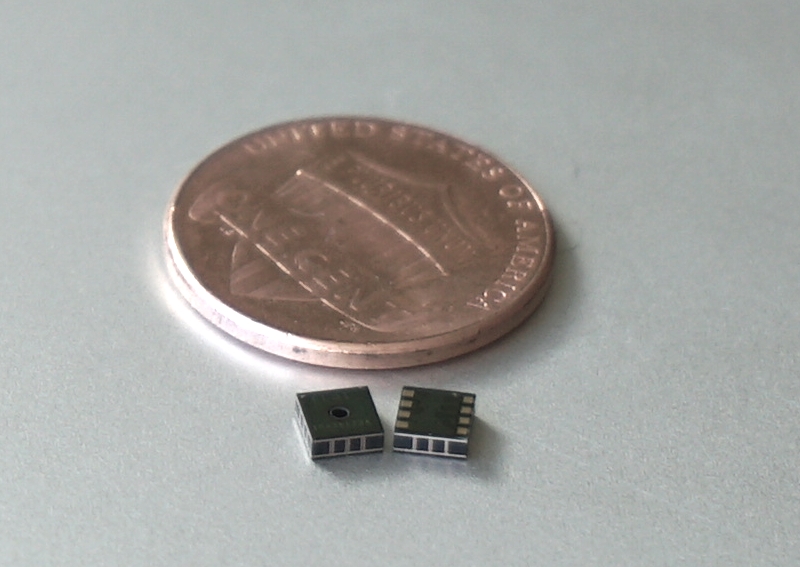
TDK Corp. is touting the Chirp SonicTrack as an inside-out six-degree-of-freedom (6-DoF) ultrasonic tracking solution for all-in-one VR. The Chirp SonicTrack from Chirp Microsystems combines ultrasonic and inertial sensor data to provide 6-DoF position and orientation tracking of a handheld controller with sub-millimeter precision over a field of view (FoV) of over 240 degrees. TDK said that the first VR system to use the SonicTrack tracking solution is a developer kit for HTC’s Vive Focus all-in-one VR system.
Chirp SonicTrack is touted as the only inside-out tracking solution, which is powered by Chirp’s CH-101 ultra-low-power ultrasonic transceiver, based on true 3D position information. The position-tracking system uses sonar by transmitting ultrasonic pulses between CH-101 sensors inside the VR system’s HMD and the handheld controllers, providing 3D position information of the controllers relative to the HMD, explained TDK. Ultrasonic tracking also translates into lower power, a wide field of view, and better optimization for mobile processors used in all-in-one VR/AR/XR systems.
Camera-based solutions have only 2D image data, which requires computation-intensive image processing from multiple cameras to estimate 3D position information, said TDK.
VR system providers can design their own 6-DoF controllers thanks to a Chirp hardware reference design and complete software stack, including a sensor fusion software library that is ready to use on Qualcomm Snapdragon and other mobile processors.
3. Synaptics Inc. R63455 display driver IC

Synaptics designed the ClearView R63455 display driver IC (DDIC) specifically for VR HMDs. It’s touted as the first display driver to offer dual-display 2K resolution combined with unique foveal transport support. The company also offers the VXR7200 VR Bridge solution that provides high-speed DisplayPort connectivity supporting full VESA DP1.4 bandwidth over tethered USB Type-C cables.
The R63455 display driver is optimized for 2,160 × 2,400 resolution @ 90 Hz, while the VXR7200 supports >2K resolution or faster refresh rates without any image loss thanks to the cabling. Together, Synaptics believes that these two solutions will deliver high-performance visual support for augmented-, mixed-, and virtual-reality HMDs in applications such as gaming, movies, commercial, and medical.
Key features include:
- R63455 VR DDIC optimized for 2,160 × 2,400 resolution @ 90 Hz
- 1,000 ppi, 2K per-eye image quality
- Foveal transport provides crystal-clear visual
- VXR7200 VR Bridge supports full DP1.4 bandwidth using AMD/Nvidia GPUs over USB-C
- Support panels >2K resolution or faster refresh rates without image loss due to cabling
4. Dialog Semiconductor SmartBond DA1469x Bluetooth Low Energy SoCs

Building on its family of SmartBond products, Dialog’s new family of SmartBond DA1469x Bluetooth Low Energy SoCs adds greater processing power, resources, range, and battery life for IoT-connected consumer applications. The SoCs feature up to 144 DMIPS, 512 Kbytes of RAM, memory protection, a floating-point unit, a dedicated crypto engine to enable end-to-end security, and expandable memories.
The DA1469x product family is touted as the company’s most advanced range of multi-core microcontroller units (MCUs) for wireless connectivity and the first in production to have a dedicated application processor based on the Arm Cortex-M33 processor, which offers greater processing applications such as high-end fitness trackers, advanced smart home devices, and VR game controllers.
In addition, the new integrated radio offers double the range, and an Arm Cortex-M0+-based software-programmable packet engine implements protocols and provides full flexibility for wireless communication. Complementing the M33 and MO+ protocol engine is a sensor node controller (SNC) based on a programmable micro-DSP that runs autonomously and independently processes data from the sensors connected to its digital and analog interfaces, said Dialog. This wakes the application processor only when needed. In addition, the devices offer a power management unit (PMU) that controls the different processing cores and activates them as needed for further power savings.
5. Toshiba Memory Europe UFS Ver. 3.0 embedded flash memory
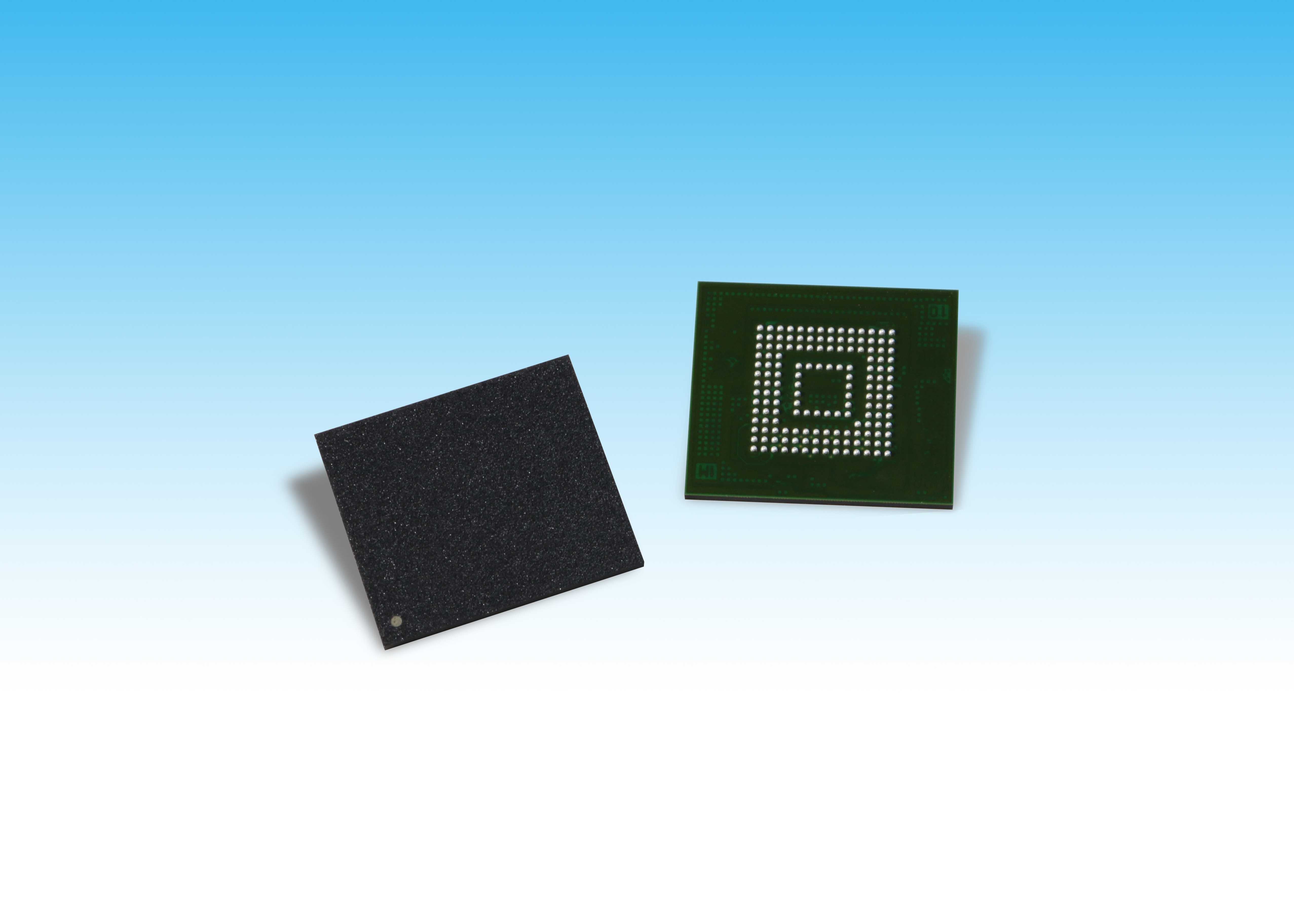
Toshiba Memory Europe GmbH (TME) is sampling the 128-GB version of the industry’s first Universal Flash Storage (UFS) Ver. 3.0 embedded flash memory devices. Thanks to its serial interface, UFS supports full duplexing, which enables both concurrent reading and writing between the host processor and UFS device.
The new memory devices integrate the company’s 96-layer BiCS FLASH 3D flash memory and is available in three capacities — 128 GB, 256 GB, and 512 GB — along with a controller in a JEDEC-standard 11.5 × 13-mm package. All three devices are compliant with JEDEC UFS Ver. 3.0, including HS-GEAR4, which has a theoretical interface speed of up to 11.6 Gbits/s per lane (× 2 lanes = 23.2 Gbps), said TME, while also supporting features that keep power consumption in check. The controller performs error correction, wear leveling, logical-to-physical address translation, and bad-block management to ease system development.
The devices’ high-speed read/write performance and low power consumption make them well-suited for VR/AR systems, mobile devices, smartphones, and tablets. Sequential read and write performances of the 512-GB device, for example, are improved by approximately 70% and 80%, respectively, over previous-generation 256-GB Toshiba devices.
6. Microchip Technology Inc. DSC613 clock family
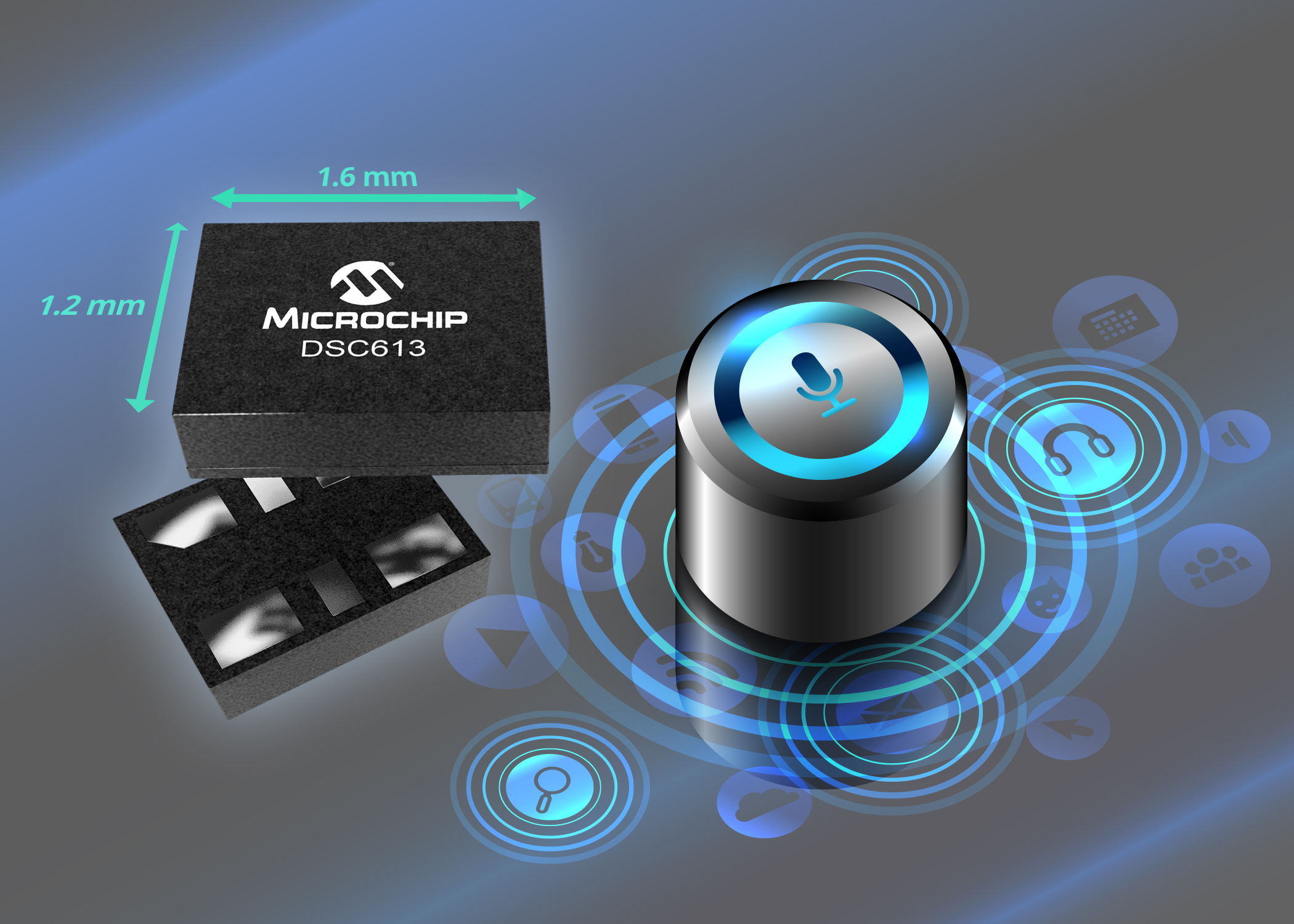

Microchip Technology claims the industry’s smallest microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) clock generator to solve one of the biggest design challenges: application size. This new device can replace up to three crystals and oscillators on a board, which reduces the timing component board space by up to 80%, said Microchip.
The DSC613 clock family eliminates the need for an external crystal by integrating a low-power and high-stability MEMS resonator. The family also incorporates two low-power phase-locked loops (PLLs) into a six-pin DFN package as small as 1.6 × 1.2 mm. Applications include digital cameras, smart speakers, VR headsets, streaming sticks, and set-top boxes.
The DSC613 family supports up to three clock outputs from 2 kilohertz (kHz) to 100 megahertz (MHz). This means that the clock generator can be used to provide a MHz main reference clock and 32.768-kHz real-time clock (RTC) for the MCU, as well as another MHz clock for functions such as connectivity and sensors in an IoT application as an example.
The two low-power fractional PLLs with AnyRate clock synthesizers enable the device to generate any frequency between 2 kHz and 100 MHz. At approximately 5-mA power consumption with three outputs running, the family provides up to 45% power savings when compared to a solution that uses three low-power quartz oscillators, said Microchip. In addition, the clock output can be turned off through the output enable pin for more power savings.
7. C&K KMT0 tactile switch
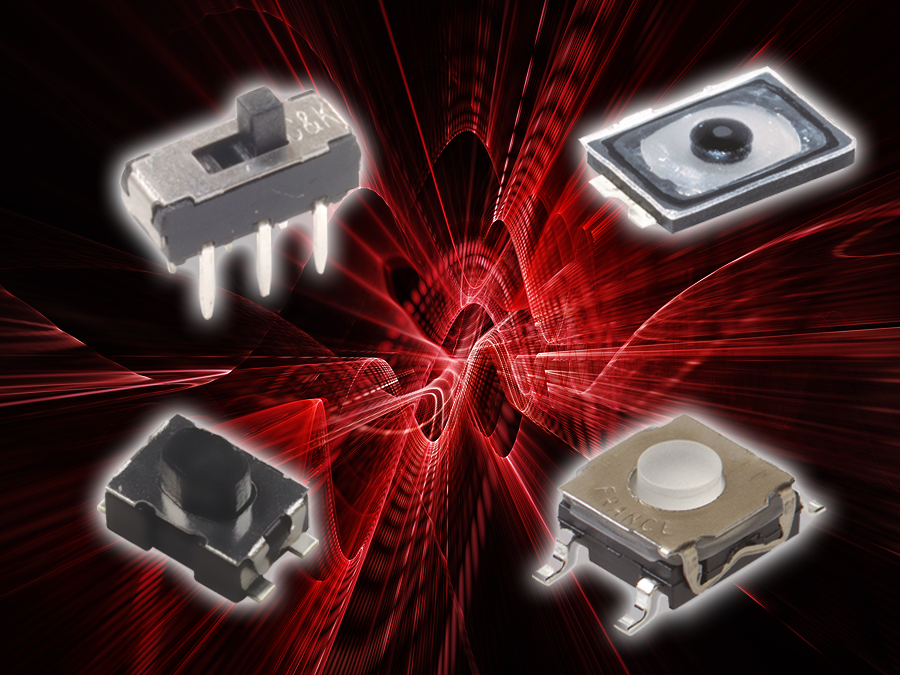
C&K offers a broad range of ultra-compact tactile switches for gaming controllers and gaming accessories . These include miniature tactile, ultra-miniature tactile, and micro-miniature tactile switches for PCB mounting. These switches can be customized for the exact sound and feel for the application.
The KMT0 series nano-miniature SMT top-actuated switch features an integrated actuator and offers the smallest footprint and thickness. Thanks to an operating life of up to 1 million cycles, excellent haptics, and the ability to withstand harsh environments and operating conditions, these switches are well-suited for gaming applications including VR headsets and mobile gaming controllers.
The KXT3 and KSC series tactile switches can also be used for mobile- and console-based gaming products. The ultra-low-profile top-actuated KXT3 tactile switch series provides a 3.0 × 2.0-mm footprint, 0.6-mm thickness, and a high number of cycles. The KSC2 and KSC4 series of sealed tactile switches are IP67-rated, have soft actuators for the haptic experience preferred by most gamers, and withstand the harsh usage conditions such as vibration and shock, said C&K.
For gaming accessories such as headphones and VR headsets, other tactile switches suited for these applications include the KMR4, PTS810, PTS830, and the side-mounted KMS.
8. Texas Instruments USB PD controllers
With fully integrated power paths, the new USB Type-C and USB Power Delivery (PD) controllers from Texas Instruments (TI) deliver smaller solution sizes and cost savings by reducing the number of external components required for computing applications, thus reducing design complexity. Claiming the industry’s first 200-W and 100-W USB Type-C and USB PD controllers, the TPS65987D and TPS65988 devices support computing applications as well as a variety of other end products, including cordless power tools, gaming, and VR headsets.
The single-port TPS65987D, designed to source 100 W of power, integrates independent 20-V, 5-A source and sink load switches. Key features include a low RDS(on) (25 mΩ) for efficient charging and reverse-current protection to protect the system and controller from overcurrent.
The dual-port TPS65988, which sources 200 W of power, provides two integrated 5-A bidirectional load switches and external power-path control to enable simultaneous 5-A source capability, said TI. The 200 W of power allows for fast USB Type-C charging while maintaining low RDS(on) , and the two integrated 5-A FET paths enable high-power applications, including PC notebooks, docking stations, and connected peripherals. Several reference designs are available.
9. Maxim Integrated MAX77714/MAX77752 PMICs

Designed to maximize performance per watt while increasing system efficiency for computationally intensive deep-learning systems on SoCs, FPGAs, and application processors, Maxim’s MAX77714 and MAX77752 power management ICs help deliver ultra-low power consumption for a range of applications including AR/VR, gaming, solid-state drives (SSDs), security, industrial IoT, cameras, and home automation hubs. These PMICs consume 40% less power than standard solutions, said Maxim, extending battery life while housed in a small form factor.
The MAX77714 PMIC delivers a complete power management solution in a compact package to enable multi-core processor-based systems to operate at maximum performance with greater than 90% efficiency at 3.6 VIN, 1.1 VOUT . The PMIC enables smaller and thinner products with a 70-bump, 4.1 × 3.25 × 0.7-mm WLP package and extends battery life up to 40% compared to standalone solutions. The device also integrates 13 regulators, including nine low-dropout linear regulators, an RTC, backup battery charger, watchdog timer, flexible power sequencing, and eight general-purpose input/outputs (GPIOs), which reduces design cycle time, component count, and BOM costs compared to discrete solutions.
The MAX77752 is a multi-channel, compact, and integrated PMIC designed for applications with multiple power rails and hot-plugging. It improves efficiency up to 90% at 3.6 VIN , 1.8 VOUT for longer battery life and includes a flexible power sequencer (FPS) to allow hardware- or software-controlled power-up, said Maxim. Like the MAX77714, it also reduces design cycle time, component count, and BOM costs through integration. The PMIC integrates three buck regulators (with high-accuracy brownout comparators), one low-dropout linear regulator, two dedicated load switch controllers, one in-rush current limiter, two external regulators to enable outputs, a voltage monitor for backup power control, and a dedicated digital output resource for logic control. The MAX77752 is housed in a 40-pin, 5 × 5 × 0.8-mm, 0.4-mm-pitch TQFN package. Evaluation kits are available for both devices.
10. MagnaChip Semiconductor Corp. 40-nm mobile OLED display driver
MagnaChip offers a third-generation 40-nanometer (nm) OLED display driver integrated circuit (DDIC) for next-generation OLED smartphone displays. The new rigid OLED DDIC supports various configurations such as FHD to FHD++, a wide aspect ratio up to 21:9, and bezel-less, edge-type, and notch-type OLED displays. These drivers can also be used in VR HMDs.
The 40-nm mobile OLED DDIC offers several improvements, including lower power consumption and improved protection against electrostatic discharge (ESD) and electromagnetic interference (EMI), compared to the second-generation OLED DDIC. It also offers enhanced compensation features that improve color and brightness uniformity.
Advertisement
Learn more about C&K ComponentsDialog SemiconductorMagnaChip SemiconductorMaxim IntegratedMicrochip TechnologySynapticsTDK AmericaTexas InstrumentsToshibaVishay Intertechnology





